Tips for using our ReferralMD Portal
If your patient does not have email please use patient@acceleratedpsychiatry.com
If your Organization does not have an NPI2, there is a bug that prevents referrals. Please enter it as a Non-Provider organization for now.
If you provide an email for your office, you will receive an invitation for a free account so we can communicate securely without faxes.
For all IV Ketamine referrals, we check the patient’s insurance coverage for Nasal Esketamine in case of financial strain for non-covered infusions.
Does my patient qualify for treatment?
Off Label use for Depression & PTSD
We work with providers to determine appropriate treatment
Can be coordinated with exposure therapy for PTSD
Indicated for Treatment Resistant Depression
Indicated for Depression + Acute Suicidal Ideation
Can be coordinated with exposure therapy for PTSD
Exact Criteria Varies by Insurer
- Check Our Insurance Grid
Indicated for Treatment-Resistant Depression
Middle Prefrontal TMS Indicated for OCD
Exact Criteria Varies by Insurer
- Check Our Insurance Grid
Guidelines for Spravato Coverage
These are our best understanding of insurance requirements to help guide the decision to initiate a referral. All final authorizations will be determined in coordination with the insurers and may differ from our chart.
We know your time is valuable. We will update this chart in realtime as we get new information from our insurers to inform your decision.
Minimum Criteria for ALL PAYORS
- Age 18 years or older Age 18 years or older
- 1+ Oral Antidepressant During Treatment 1+ Oral Antidepressant During Treatment
- ∅ Hx Psychosis OR Benefits Outweigh Psychosis Risks∅ Hx Psychosis OR Benefits Outweigh Psychosis Risks
- Spravato Must be Administered by a Psychiatrist Spravato Must be Administered by a Psychiatrist
- Inadequate Response ≥2 CLASSES of antidepressant + 1 augmentation Inadequate Response ≥2 CLASSES of antidepressant + 1 augmentation
How can ketamine benefit anxiety therapy?
Ketamine does not facilitate “going deeper” or better engagement of exposure therapy targets. Instead, ketamine and NMDA antagonists delete recently activated fears by disrupting their “reconsolidation”. Since reconsolidation takes place AFTER psychotherapy, so should ketamine treatment. Reactivated fears are most vulnerable to ketamine in the first 2 hours after psychotherapy. Memory storage continues and can be disrupted up to about 4 hours after exposure therapy, especially since IV and nasal ketamine rapidly enter the brain.
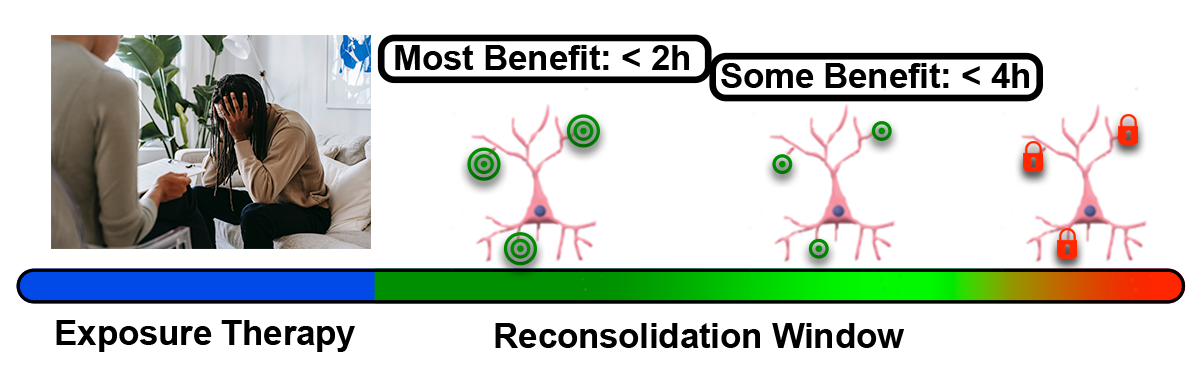
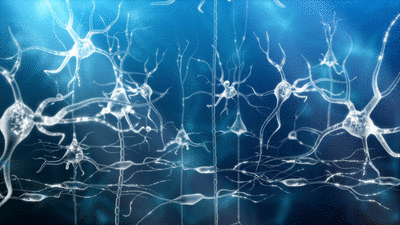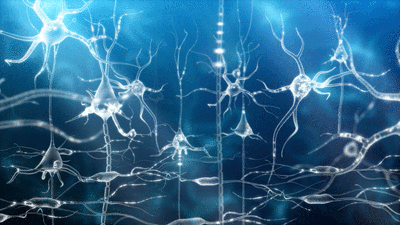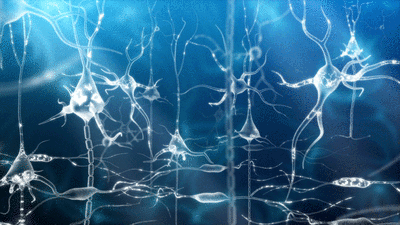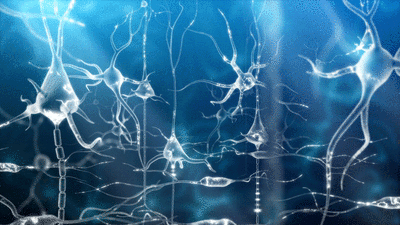
Successful exposure therapy reactivates fear memories that must be saved again in a process that requires protein synthesis to reinforce dendritic spines. This calcium-mediated reaction can be synapse-specific because it is triggered by glutamate activating NMDA receptors at a given synapse, while the fear cell is already firing from synapses representing other features of the memory. Blocking the NMDA with ketamine prevents storage of previously-connected fear cues and contexts that constitute the original fear memory, effectively erasing it.
A recent study attempted to use NMDA blockade only after “good” therapy sessions, as rated subjectively, was less effective than doing it every single time, suggesting that a “good” reactivation of the fear may not be recognized by you or your patient. If you are a psychologist or exposure therapist and would like to coordinate your treatments with your patient’s ketamine treatments, we recommend that the therapy precede the ketamine visit by no more than 4 hours. Research predicts that ketamine only requires 1-2 treatments to eliminate the biological fear, but patients will require further therapy and likely in-vivo exposures for subjective fear to subside.
Essential Considerations for Psychotherapy
Prescribing Concerns
While large, long-term studies are not yet available, the preponderance of studies show no increase in psychotic episodes or symptoms outside of acute treatment sessions. As initially described by Krystal and colleagues, and summarized in recent systematic reviews, positive psychotic experiences during the dissociative episode are mild and self-limiting within 30 min of the end of the treatment.
Hypertension must be well controlled on the current regimen. Referring providers must provide the most recent blood pressure and pulse measurements taken in a medical office. At the start of each treatment, patients with resting blood pressure above 140 mmHg systolic and 90 mmHg diastolic will not receive the ketamine treatment. Referring physicians should anticipate a rise as high as 20 mmHg systolic and 5 mmHg diastolic when considering the cardiovascular fitness for ketamine treatment.
Patients undergo continuous heartrate and blood pressure monitoring throughout the treatment. Comfortable, wireless monitors measure this at the wrist and index finger of one hand. All patients are monitored by closed circuit camera to minimize interruption of dissociative experiences. Expert nursing and medical staff are ready to adjust infusions, calm patients, or administer antihypertensive medications if required.
Prescribing Concerns
While large, long-term studies are not yet available, the preponderance of studies show no increase in psychotic episodes or symptoms outside of acute treatment sessions. As initially described by Krystal and colleagues, and summarized in recent systematic reviews, positive psychotic experiences during the dissociative episode are mild and self-limiting within 30 min of the end of the treatment.
Hypertension must be well controlled on the current regimen. Referring providers must provide the most recent blood pressure and pulse measurements taken in a medical office. At the start of each treatment, patients with resting blood pressure above 140 mmHg systolic and 90 mmHg diastolic will not receive the ketamine treatment. Referring physicians should anticipate a rise as high as 20 mmHg systolic and 5 mmHg diastolic when considering the cardiovascular fitness for ketamine treatment.
Patients undergo continuous heartrate and blood pressure monitoring throughout the treatment. Comfortable, wireless monitors measure this at the wrist and index finger of one hand. All patients are monitored by closed circuit camera to minimize interruption of dissociative experiences. Expert nursing and medical staff are ready to adjust infusions, calm patients, or administer antihypertensive medications if required.
Should Patients Hold or Change Medications?
TMS/TBS Considerations
Please avoid medication changes during treatment.
If a change is necessary, please inform our psychiatrists.
Medication & substance use changes can affect the excitability of the brain.
This means new thresholds may need to be calculated.
Re-mapping TMS targets is time-consuming and painful.

Ketamine Concerns
No medications fully contraindicated
Even MAO inhibitors are safe because ketamine has no serotonin reuptake inhibition
Benzodiazepines have been shown to reduce benefits of ketamine.
Noradrenergic medications may amplify hypertensive effects of ketamine.
Please ensure sufficient antihypertensive treatment to contain this rise.





